Just because a motor can lift a ton doesn’t mean it can do it all day.
To drive a 1-ton load continuously, a motor with 1.5–2.2 kW (2–3 HP) is typically required, depending on lifting speed, duty cycle, and system efficiency. Overload protection is critical.
I’ve seen motors burn out not because they were weak—but because they were used for the wrong application class. Let’s break down what your setup really needs.
[Table of contents]
- How much can a 1-ton motor lift?
- What motor type is best for electric hoists?
- What power rating is suitable for continuous lifting of 1 ton?
- How do duty ratings affect motor selection?
- What is motor overload protection and why does it matter?
- How to match power supply with your motor requirements?
How much can a 1-ton motor lift?
The lifting capacity is just one part of the equation.
A 1-ton rated hoist motor can lift up to 2,000 lbs—but the real question is how often and how long it can do it.
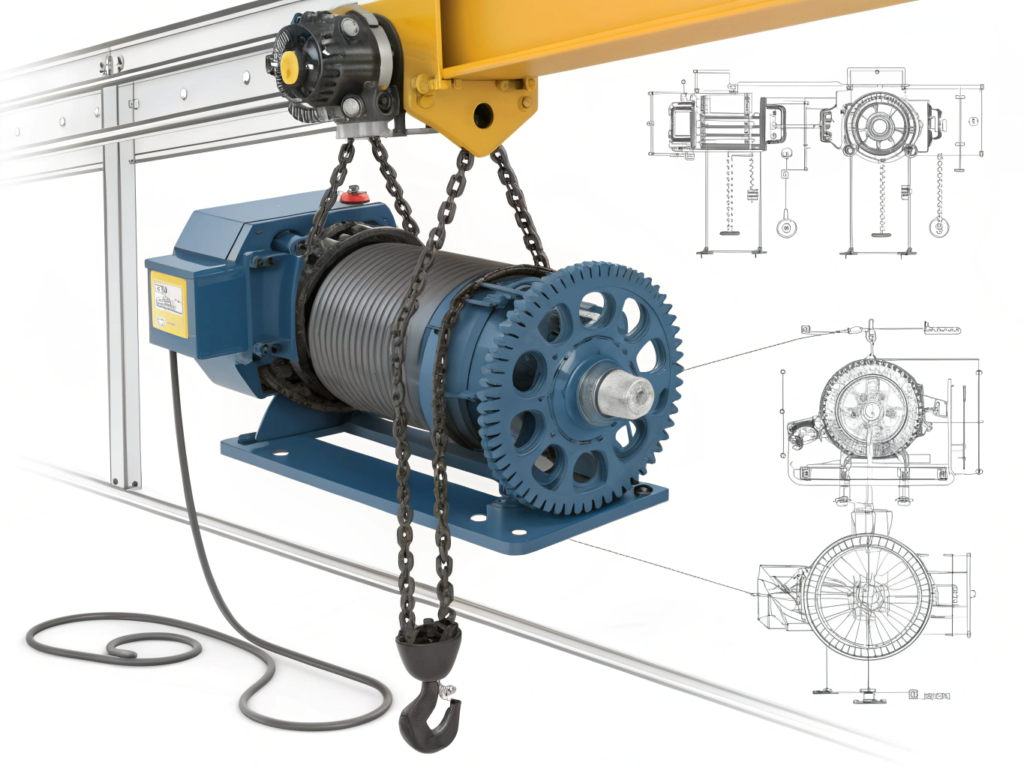
Dive Deeper
- Static load rating tells you what it can lift once.
- Duty cycle rating tells you if it can repeat that task every 5 minutes for 8 hours.
For repetitive lifting in industrial environments, a 1-ton hoist should be paired with a motor that offers thermal protection and a duty rating of H4 or higher.
What motor type is best for electric hoists?
It depends on your load pattern and power source.
Three-phase induction motors are most common for industrial hoists due to their efficiency, torque, and durability under load.
Dive Deeper
| Motor Type | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Induction (AC) | Continuous-duty hoisting | Durable, handles overload well |
| DC Motor | Variable speed / precision | Good for compact or mobile units |
| Servo Motor | High-precision applications | Expensive, uncommon for 1T use |
Most 1-ton hoists use AC squirrel cage motors, often paired with mechanical brakes and gear reducers.
What power rating is suitable for continuous lifting of 1 ton?
Here’s the rough power-to-load rule.
A 1.5–2.2 kW motor (about 2–3 HP) is typically suitable for long-duration lifting of 1-ton loads, depending on lift height and frequency.
Dive Deeper
| Load Weight | Recommended Motor Power | Duty Rating | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 kg | 0.75–1.1 kW | S3–25% | Light, intermittent use |
| 1 ton | 1.5–2.2 kW | S3–40% or H4 | Continuous or production line lifting |
| 2 ton | 3.0–4.0 kW | H4 or M5 | Requires advanced thermal protection |
Factors to adjust:
- Lifting speed (m/min)
- Gearbox ratio
- Electrical efficiency
- Ambient temperature
How do duty ratings affect motor selection?
Duty rating defines the “real” capacity of your motor.
Duty ratings (like S3 or H4) describe how long a motor can operate under load without overheating.
Dive Deeper
| Duty Class | Operating Pattern | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| S2 | Short-time only | Occasional lifts, <10 min |
| S3 | Intermittent operation | Workshop lifts, 15–40% load cycle |
| H4 / M5 | Continuous duty | Factory conveyors, production hoists |
Always match your motor’s duty rating to your expected operating time. Underestimating this is the #1 reason motors fail early in industrial setups.
What is motor overload protection and why does it matter?
Overload protection prevents your motor from overheating or burning out.
Overload protection uses sensors or thermal relays to cut power when current exceeds safe levels for a set time.
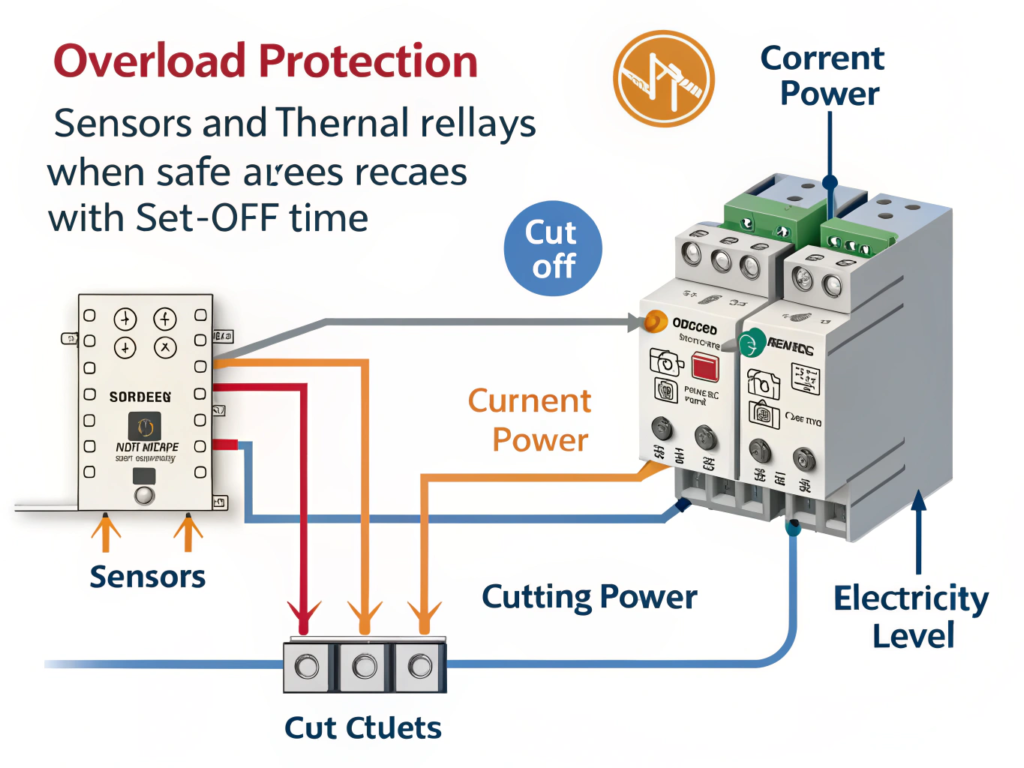
Dive Deeper
Good hoists come with:
- Thermal relays to detect overheating
- Current sensors to trip when overload is detected
- Manual reset or auto restart logic
This protection is critical when hoists are operated in high-temperature, high-cycle, or 24/7 environments.
How to match power supply with your motor requirements?
Power type and voltage must match the motor’s input specs.
Most 1-ton industrial hoists run on 220V–480V three-phase, but some light-duty models use 110V single-phase with limited cycle duration.
Dive Deeper
| Voltage | Phase Type | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 110V / 120V | Single-phase | Light-duty hoists, portable work |
| 220V / 240V | Single/3-phase | Medium-duty, small factories |
| 380V / 480V | Three-phase | Industrial-grade hoists, 24/7 operation |
Always check your site’s available power and confirm with the supplier if the hoist supports your grid. Some motors are dual-voltage but may need rewiring.
Conclusion
For a 1-ton load, it’s not just about lifting—it’s about lasting.



